How does Amazon use Time Based Competition?
Introduction
Time based competition is a very important concept in the academics of supply chain management and is an emerging trend which everyone is focusing on. In the words of Barnes, (2014) it is a major source of competition for many organisations and helps in value creation in the supply chain process.

The exact part where time based competition is applied is the
logistics industry which is involved with the transportation of goods and
services and also its distribution and sales. In the modern competitive world,
this is of crucial importance because the time saved in the logistics process
can enhance the delivery time, which is an advantage to the buyer as well as
the supplier. Baah, (2019) see it as an
economic benefit which influences the organisational performance and impacts
the sales of the buyer. The main goal of time based competitive strategies is
optimizing the logistics process for better efficiency. An essential part of
this logistics process which uses the time based competition strategies is the
speed of service, the better warehousing operations, distribution to various
centers, and others. Technological advancements have also enabled real-time
data so that shipments can be tracked and errors reduced. This facilitates
first-hand handling of the logistics problems if any.

It
is said that in tough competitive times, globalization is always increasing and
hence market dynamics are also changing. Information and resources are now
available to everyone. In such a situation time is of the essence and the
customer satisfaction criteria now depend on how fast goods can be delivered to
them. Most manufacturing companies stay ahead of the competition by offering a
faster delivery lead time. Therefore it is essential for companies to focus on
the supply chain process, especially on logistics operations. Carbone & Gouvernal, (2017) are of the
opinion that many international companies have improved their time based
competition strategies by listening to consumer demands, other known as VOC or
Voice Of Customers. This is the essence of the competitive advantage!
How
organisations have evolved to make their supply chain processes faster?
It
is interesting to note that the greatest weapon in the logistics process has
been the logistics service providers or the LSP. They are usually third party
organisations hired by the manufacturing company to take care of the logistics
part. According to researchers Carter &
Rogers, (2008), this falls under outsourcing strategy which is a very
important component of the supply chain process. Many companies crucially
analyze and assess their logistics operations before hiring the services of
LSP. Christopher, (2016)here pointed out
that there are two main categories of outsourcing which are responsible for
time based competition. Firstly, it is non-core outsourcing which represents areas
like HRM, IT skills and logistics, and core outsourcing which represents
departments like design, manufacturing, packaging, and others. It is important
to note here that the success of time based competition depends on which
category the organisation focuses on. The analysis must be done according to
external and internal factors which an organisation faces.

Donald Rhodes, (2015)states that that
outsourcing availability in logistics is a proven and effective measure in
reducing inconsistencies and errors in the operational process. In this stage,
prioritizing becomes important for organisations as the success depends on it.
Thus, it can be said that time based competition is a crucial part of the
supply chain process. It is also a part of the operations strategy whose main
goal is to optimize the production performance and minimize the cost involved
in the process as well. Having said this it is evident that time based
competition also influences overhead cost, the travel time, the sales and
distribution process, and more. The most glaring example is the manufacturing
sector, be it any industry like leather, FMCG, and others. Export and import
companies largely rely on LSP to improve delivery time and increase the value
in terms of faster ETA and ETD.
Going
through the academic literature, it is seen that outsourcing activities mainly
constitute transportation and warehousing management. In simple words, focus on
these activities by an LSP enables the company to put more focus on the
production and quality management process
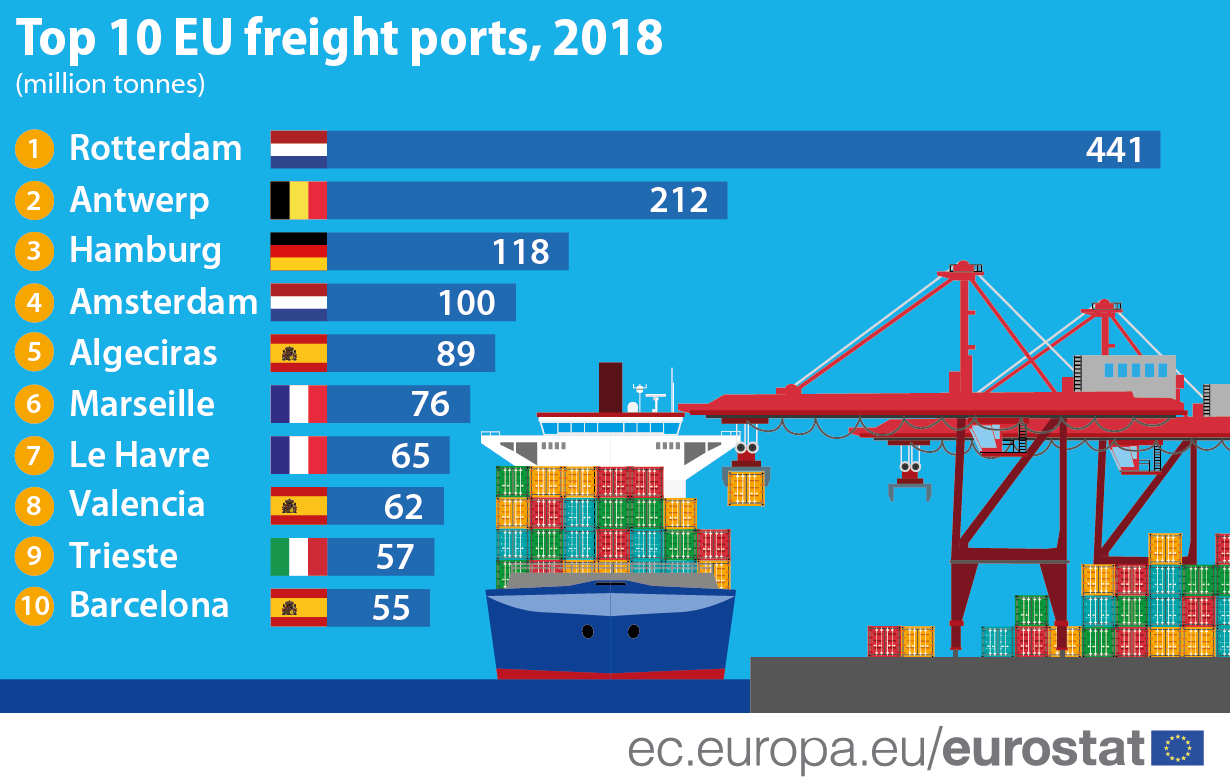

To
cite an example, the port of Rotterdam in the Netherlands can be taken into
consideration, which is the largest and the busiest seaport in Europe. It acts
as the prime logistics hub and warehousing and storage facilities for all
European companies. Countries like Germany, Belgium, Netherlands, Spain,
France, Austria, and Bulgaria all take the services of this port for their
shipments. Statistical figures indicate that 469 million tons of cargo are
received annually by Rotterdamin Europe
Literature
Review
Many
researchers like Jamieson, (2013) are of
the opinion that when a project is carried over in the short term, outsourcing
may involve handling the control of public services to private firms. This is a
very important move for the organisations as according to the researcher it is
the source of competitive advantage. According to Schönberger, (2019) also the dependent variable here is the capacity
expansion decision of an organisation. It can be said that when production
exceeds the existing capacity of an organisation, it decides to expand so as
not to constraint parts of the supply chain process. This has been increasing
in recent years due to the over increasing demands of the market. Having said
this it is important to note that capacity expansion decision is an important
factor that is linked to time based competition. Heitmann et al, (2017) also mention that the relationship between
outsourcing and the capacity to expand depends on some influencing factors,
which impacts the role of cost strategies and innovation. These factors act as a
moderator between the two, giving an organisation the competitive advantage it
needs. Innovation must be pointed out as an important influencing factor, as
pricing and cost strategies depend on innovation in the supply chain process;
the more innovation in technological advancement, the more competitive the unit
cost of a product is. Innovation is also directed to outsourcing, where
e-services further make the system efficient. Researchers Liu, Nie, & Yuan, (2019) here cite that
innovation in outsourcing can create a sustainable economy by creating a risk-free
international market and introducing flexibility in the existing domestic
market scenario.

As
competition forms the integral goal of the time-based strategies, it must be
mentioned here that time has become of increasing importance as consumers rely
on time-based service, and organisations must use this in creating value to its
products. For this reason, time based competition strategies must be taken in
accordance with the corporate strategies of the organisation. Rich & Hines, (2016) point out that since
the intent is value creation, the scale of time compression must be considered
especially if a company is operating on a global basis. Thus the researchers
state that the impact of a commercial advantage here is the reduction of
commercial risks in the logistics process. Yu, (2019)
further points out that time based competition was not seen until the 1900s.
Logistics then was only carried out by a group of industries, who had dedicated
the lowest possible budget for the process. It is only after World War II that
timely delivery became of crucial importance as competition then was as close
to survival in war times. The process gained momentum, after the 1900s, as
technological advancements increased and the World Wide Web came into being. He
states that with this advancement, companies differentiated themselves from
their competitors by focusing on cost-quality and timely delivery.
Several other researchers like Purvis, et al., (2015) also mention that globalization further contributed to creating time based strategies competition was increased and consumer, as well as the supplier, focused on the value of time. They called the process production industrialization; the supply chain process becomes more commercial and industrial as time becomes an integral issue. They further mention that there are two categories which are affected the most by time based competition; first is the scope of the outsourcing that each organization had and second, is how critical a task is that is carried out through the outsourcing process. As mentioned earlier the scope here depends on various internal and external factors. While some organisations take the help of third-party LSP, some stick to their own department of logistics. No matter what the process it, all strategies are directed to speeding up the time in the supply chain process, especially logistics. Studies have also proven that proper handling of the process can improve the overall organisational performance.
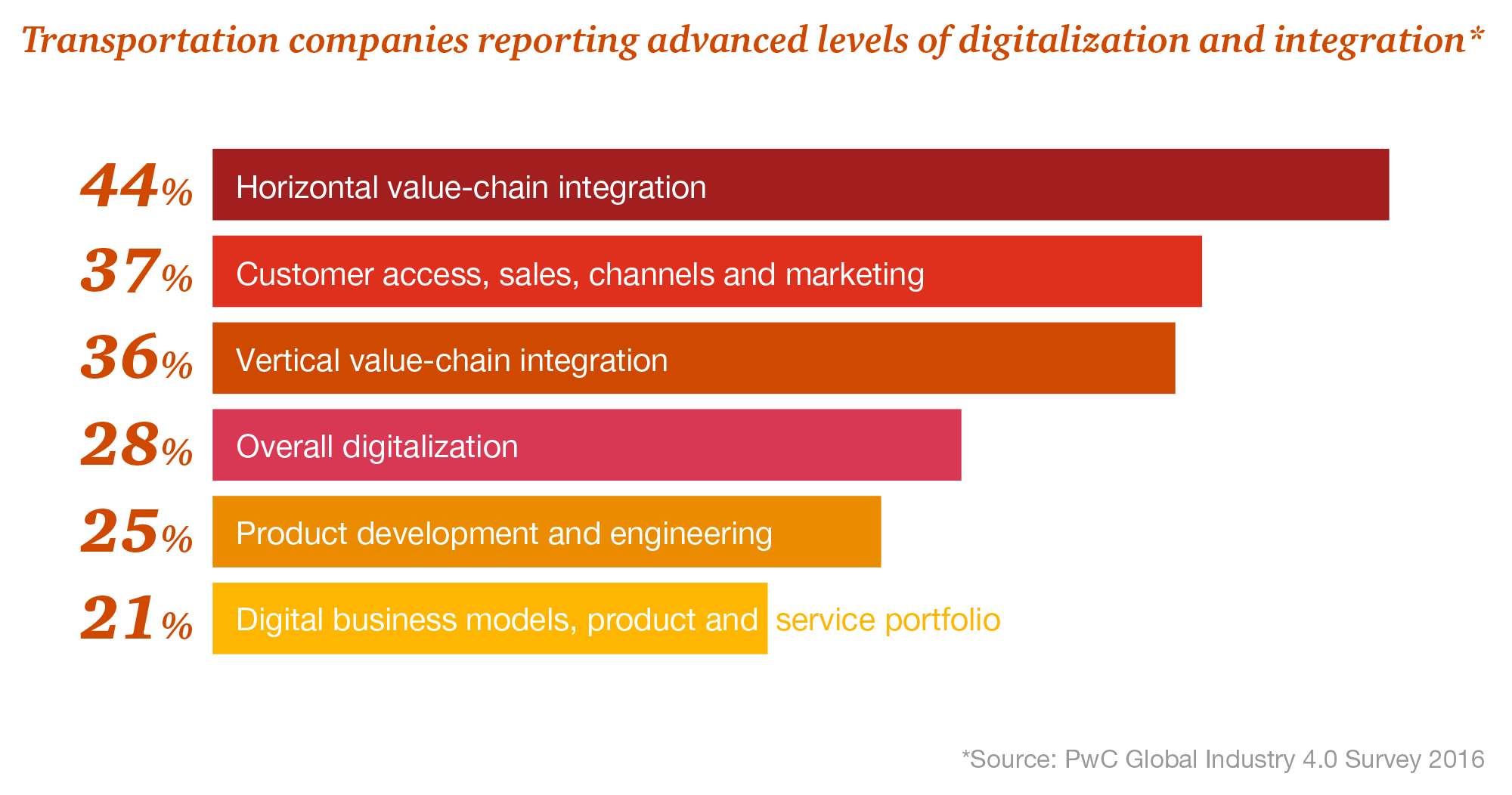
Rae, (2017) here pointed out several issues
that the logistics department of the UK industry faced when dealing with
Brexit. He says that since logistics depended on delivery and price, much of
the buyers were affected as prices hiked and delivery was delayed. He says that
in such a price and time-sensitive market it is essential that companies gain
competitive advantage by offering time guarantees. Taking the current scenario
of Coronavirus pandemic into account, people highly understand the importance
of timely deliveries. While most people are locked at home, 75% of the public
depend on e-commerce solutions to get goods delivered

Taking
Europe into consideration, certain studies have pointed out various LSP that
provide time based competition. Logistics companies like Bpost, PostNL, BRT
Corriere Espresso, Asendia, and Mondial Relay deliver almost 6000 deliveries in
a day. As mentioned earlier Amazon UK, is at the top of the list when it comes
to daily eCommerce. For other deliveries, Royal Mail and Hermes UK are major
logistics players which provide extremely competitive and timely deliveries.
Hermes UK is said to deliver around 10,000 eCommerce couriers and 4500 personal
parcels a month

Application
of the ideas and concepts of time-based competition by Amazon
Amazon
was chosen to be an organisation on which the application of the concepts of
time-based competition would be studied, in order to gain an insight into how
companies utilize these concepts in the eCommerce scenario.
Amazon,
as it is known, is an eCommerce giant which delivers products all over the
world. It is based in Seattle and has over 750,000 employees worldwide. It is
deemed to be the largest company in the world in terms of internet revenue

Elnahla, (2016) here pointed out that
one of the crucial applications is the technological advancements that the
organisation took up. Essentially, it is the largest virtual marketplace holder
to work on AI and cloud computing platforms. It also uses digital streaming to
conduct video conferencing for its retailers, so that more product line and
more trusted suppliers can be added. Prince
& Slobin, (2015) here also point out that Amazon time based
competitive strategy is also based on the diversification methods that it had
innovated. Simply, put Amazon Prime members are entitled to two-day delivery,
one-day delivery, and even 8 hour delivery on special cases. In addition to
this, the company has Amazon twitch, Amazon Music, Amazon web services, Amazon
Publishing, and others which are all linked to provide the highest customer
service and delivery like no other company! Although the company has been
criticized for technological surveillance overreach, Amazon still sticks to its
tech methods to gain the highest time based competition in the market. One such
advancement was reached when Amazon used drones to deliver in places where
human reach is impossible. The wing is called Prime Air and goods are delivered
in scared locations in less than 30 minutes
Amazon,
unlike other companies, does not use third-party LSP but rather they have their
own logistics department and warehousing facility which is used in their supply
chain process. Initially, the company had launched two fulfillment centers
only, one in Seattle and the other in Delaware.
However, Amazon UK has its center in Glenrothes in Scotland. This center
has especially become important after Brexit, as earlier Amazon used the
fulfillment center in Germany for its deliveries to the UK

Effectiveness
of the concepts of time-based competition taken by Amazon
The
effectiveness of Amazon can be solely credited to innovation and technological
advancements, which provide real-time data regarding consumer behavior and VOC
to improve its time based competition. According to Stevens, (2017), Amazon is expected to sell almost 12.6 billion
products in the year 2020. This accounts for nearly half of the online retail
in the UK. It has also been said that fulfillment centers will have better data
centers for its cloud computing business. The company currently hires contract
drivers all over the nation through its Flex delivery service and the hiring is
just expected to increase over the years
Researchers
Weber & Badenhorst-Weiss, (2016) say
that Amazon has gone beyond human capacity to drive its profits by optimizing
the fulfillment centers in various regions. Studies suggest that the company
spends USD 1.5 billion on shipping per day, just reorganizing and optimizing
every level of the logistics process. Thus, the dedication towards time based
strategies is noticed! Not only this, capacity expansion decision taken by the
firm has further promoted The Climate Pledge according to Amazon Press Center, (2019), where Amazon is
achieving zero carbon emissions by the year 2040. Although this is a very
complex process, Amazon believes that advancement in technology is possible to
achieve this goal. Thus, time based competitive strategies also paved the way
for green goals by the organisation. It is also important to point out that the
corporate goal of customer obsession has further made this possible, as the
company was dedicated to providing the highest level of customer satisfaction
possible.

Conclusion
To
conclude it can be said that time based competition is an important part of the
supply chain process, which has impacts on the operations strategy, the
capacity expansion decision, and most importantly outsourcing. Researchers Esteban & Annachiara, (2019) state that
most of the time based competition has been based on computation technologies,
especially in large scale industries and Amazon, is the right example for it.
The stress on computation and automation is what made Amazon the leader in the eCommerce
business. It is, therefore, safe to say that time based competition is an
emerging trend which is bound to get stronger, as customer expectation
increases.
References
Amazon Press Center, 2019. Amazon Co-founds The
Climate Pledge, Setting Goal to Meet the Paris Agreement 10 Years Early, Paris:
Amazon Press Center.
Amazon.com, 2020. Amazon Prime
Air. [Online]
Available at: https://www.amazon.com/Amazon-Prime-Air/b?ie=UTF8&node=8037720011
[Accessed 28 April 2020].
Ashayeri, J. & Yuan, X., 2016.
Capacity expansion decision in supply chains: A control theory application. International
Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing , pp. 356-373.
Baah, C., 2019. Green Logistics
and Organisational Performance: Exploring Time-Based Competition as a Missing
Link. Journal of Supply Chain Management Systems, 8(3), pp. 25-36.
Barnes, S., 2014. Objectives of
the Supply Chain, s.l.: IBIS Inc. .
Carbone, V. & Gouvernal, E.,
2017. Supply Chain and Supply Chain Management: Appropriate Concepts for
Maritime Studies. 2nd ed. s.l.:Taylor & Francis.
Carter, C. R. & Rogers, D. S.,
2008. A framework of sustainable supply chain management: moving toward new
theory. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics
Management, 38(5), pp. 360-387.
Christopher, M., 2016. Logistics
& Supply Chain Management. 5th ed. London: Pearson UK.
Donald Rhodes, M. J. D., 2015.
Socially Responsible Supply Chain Management for a Competitive Advantage. New
Perspectives on Corporate Social Responsibility, pp. 321-340.
ecommercenews.eu, 2019. Ecommerce
logistics companies in Europe, s.l.: Ecommerce News EU.
Elnahla, N., 2016. From the
Panopticon to Amazon Go: An Overview of Surveillance in Retailing, Ottawa:
Carleton University Publications.
Esteban, K. & Annachiara, L.,
2019. A systematic review of sustainable supply chain management in global
supply chains. Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 207, pp.
1084-1098.
Fernie, J. & Sparks, L., 2018.
Logistics and Retail Management: Emerging Issues and New Challenges in the
Retail Supply Chain. 5th ed. s.l.:Kogan Page Publishers.
Heitmann, M. et al., 2017.
Framework to decide for an expansion strategy of a small scale continuously
operated modular multi-product plant. Chemical Engineering and Processing:
Process Intensification, pp. 74-85.
Jamieson, D., 2013. Public
Interest Group Challenges Privatization Of Local, State Government Services, s.l.:
The Huffington Post.
Jeff Bezos, 2019. Amazon.com
Inc.. [Online]
Available at: http://media.corporate-ir.net/media_files/irol/97/97664/reports/Shareholderletter97.pdf
Liu, J., Nie, J. & Yuan, H.,
2019. To expand or not to expand: A strategic analysis of the recycler's waste
treatment capacity. Computers & Industrial Engineering, pp.
731-744.
Magazine, D. T. G. L., 2020. When
disaster strikes: How do you build resilient supply chains?, s.l.: DHL
International GmbH.
Martin, M., 2017. Supply Chain,
s.l.: Hellenic Bottling Company.
Port of Rotterdam Authority N.V. ,
2020. Our Port. [Online]
Available at: https://www.portofrotterdam.com/en/our-port/facts-figures-about-the-port
Prince, M. & Slobin, S., 2015.
How 20 Years of Amazon Changed Retail, s.l.: The Wall Street Journal.
Purvis, L., Spall, S., Naim, M.
& Speigler, V., 2015. Developing a resilient supply chain strategy during
‘boom’ and ‘bust’. Journal of Production Planning and Control, pp.
579-590.
Rae, J. O., 2017. IMPACTS OF
BREXIT ON DEMAND AND SUPPLY OF LABOR, s.l.: Academia.
Rich, N. & Hines, P., 2016.
Supply-chain management and time-based competition: the role of the supplier
association. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics
Management, 27(3), pp. 210-225.
Routley, N., 2018. Amazon's
Massive Distribution Network in One Giant Visualization, s.l.: Visual
Capitalists.
Schönberger, D. I. T., 2019. Global
Supply Chain and Operations Management. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer.
Schoolov, K., 2019. What it’s
really like to be an Amazon Flex delivery driver as Prime one-day shipping
expands, s.l.: CNBC.
Searates.com, 2020. Sea ports
of United Arab Emirates. [Online]
Available at: https://www.searates.com/maritime/united_arab_emirates.html
[Accessed 27 April 2020].
Sisson, P., 2019. Amazon’s
bonkers warehouse and delivery empire, by the numbers, s.l.: Curbed.
Staff, E., 2018. Supply Chain
Management And Sustainability Practices : Coca Cola Australia, s.l.: My
Assignment Help.
Stevens, L., 2017. How Amazon
Can Make or Break Holiday Retail, s.l.: Wall Street Journals.
Weber, A. & Badenhorst-Weiss,
J., 2016. Time-based competition as a competitive strategy for online grocery
retailers. Journal of Contemporary Management , 13(1), pp. 433-460.
Yawar, A. S. S., 2017. Management
of Social Issues in Supply Chains: A Literature Review Exploring Social Issues,
Actions and Performance Outcomes. Journal of Business Ethics, 141(3),
pp. 621-643.
Yu, Q., 2019. Supply chain
management of new coffee retail enterprises from the perspective of value
co-creation—Taking Laibei coffee as an example. Paris, Atlantis Press.

Comments
Post a Comment