Supply Chain Management Process of Starbucks

More
and more companies are concentrating on creating a sustainable supply chain
process in their operation network and using the resources to its maximum
capacity. A growth of conscious consumers has further facilitated this process
as more and more consumers want companies to lay stress on environmental and
sustainable factors. The actual transformation occurred in the year 2008 and
the main approach used by the company was the integration of various processes
that allowed them to achieve a long term profit. These processed were social,
environmental and economic process whereby Starbucks could develop a proper
SSCM network
The Findings
After
recognizing and evaluation the current supply chain which Starbucks had at that
point of time, the Senior Vice President Gibbons found out that more than half
of the delivery of raw material to the store were arriving late. Gibbons
visited several Starbucks store himself and analyzed that the employees were
not paying much attention to when and how the raw materials arrived. Thus there
was clearly room for improvement. He also analyzed the cost process and
recognized that the main factor for cost inflation was the involvement of third-party
logistics. Starbucks outsourced almost 65% of its ingredients in order to speed
up the operations process. But in doing so, the agreements, contracts,
transport cost were causing delays and cost inflation of the products
Operational Strategy and Macro Environment
Although
the findings and the three-step plan were pretty direct, the design of each
part of the process was extremely complicated according to Gibbons. He tried to
simplify the entire process so that the whole system would fall into four basic
structure; plan, source, make and deliver. For example, if an employee were to
be involved in planning, he or she would be put under an umbrella of the planning
group, which would involve planning as a whole; be its production planning,
recipe planning or packaging planning. The sourcing activities were grouped
into two areas of ‘coffee’ and ‘non-coffee’. This was an easier and direct
method understandable to all. Statistical data showed that Starbucks spent
almost 600 million US Dollar on the sourcing of raw materials just for coffee.
The ‘non-coffee’ sourcing amounted to 2.5 billion US Dollar annually

The
manufacturing team at Starbucks also devised a more efficient model whereby
they could deliver coffee beans to the processing plants in a timely manner.
Starbucks opened processing plants in areas where the coffee originated. This
was one of the critical processes that reduced time and cost and increased
efficiency in a major way. According to Schönberger
et al (2019) Starbucks already owned three coffee plants in the US, the
fourth one in Columbia. Attempts and planning were made to open in other areas
of Africa and Latin America, where it sourced its coffee from. Additionally,
the company opened a plant in Amsterdam, the Netherlands for its coffee
processing in Europe and also developed 24 new co-suppliers for various raw
materials. In the cost analysis process, Gibbons saw identified that
transportation, logistics and distribution made up the major part of the expense.
The reason was inevitable because its coffee was sourced from various parts of
the world like Ghana, Venezuela, Uruguay, China, the Middle East and other
regions. This proved to be the most challenging part of Starbucks. Data
indicated that per week Starbucks had almost 70,000 to 80,000 international
delivery made mainly by sea shipment.
The
solution here again was the introduction of a single logistics system, which
would bring processed coffee beans from all over the world in sea shipments to
Europe, UK and the US. From the port, the green beans would be transported to
the storage sites which were then taken to roasting plants. After they were
roasted, they were packed and transported to the distribution centres
regionally. The distribution centres were managed by third-party companies, who
delivered the products to the retail outlets. Contract rates of these third-party
companies were reviewed and negotiated for better pricing. Clear cost metrics,
production metrics and the service metrics were clearly outlined.
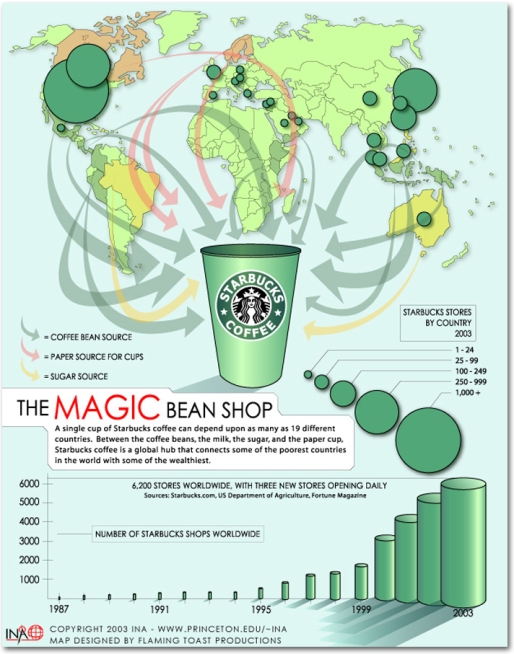
Sourcing Map of various products at Starbucks
Key Requirements, Capabilities and Challenges
In
order to cope up with the above-mentioned strategies, Starbucks had to
formulate certain key requirements which they needed to maintain at all cost.
One of the areas that were mentioned earlier was the fact that the employees
working at the retail store did not pay attention to when and how the raw
materials arrived. This clearly proved a need for proper training. Although the
training was provided to all employees, certain gaps were identified which made
them lose interest in all parts of the process. To quote what Howard Schultz
said, “these people are not only the heart and soul but also the public face of
the company. Every dollar earned passes through their hands.”
The
training of the employees was increased to being more than just a server at a
retail store. They were encouraged to learn more about speciality coffees and
their origin. Employee focus was directed to this by increasing the health care
benefits of everyone who were working for 20 hours or more per week. By doing
so, they not only attracted higher quality employees but also improved the
turnover rate and the overall cost spent on the employees. CSR activities were
also introduced at the various retail outlets. Various other plans like the
Bean Stock were introduced, which would grant stock options to every employee,
from top managers to servers

The
quality of coffee beans also had to be maintained as cost in logistics and
deliveries were reduced. Starbucks bought about a social change in the
suppliers by conducting tie-up with conservation organisations such as
Conservation International. This strategic collaboration facilitated the
establishment of CARE (Coffee and Farmer Equity Practices). This practice
ensured farmers were treated ethically and had the chance to improve their life
by offering high-quality coffee
The
major challenges that were faced while improving the supply chain process were
dealing with logistics and the distribution centres. The huge volume of their
business proved to be quite tough to handle. The distribution centres alone
were 200,000 to 300,000 square feet in size. Deliveries made per week were also
70,000 in numbers. The main areas of the challenge here were the product
transition, the introduction of new products and the promotion of the same

Analysis and Evaluation
From
the above discussion, it is clear that Starbucks developed many strategies
which would improve their supply chain processes. These strategies were just
only a part of other strategies that were incorporated along with the changing
time. However, the most important factor that Starbucks developed in the minds
of its customer is the feeling of community. Many scholars like Esteban et al(2019) state this feeling as the
‘third place’. This ‘third place’ was a representation of a corner or a place
where customers could forget their daily routine and sit and relax with a quiet
cup of coffee. The design analysis as mentioned earlier here is important as
store designs were made keeping in mind this feeling of a special place. Other
four Vs also contributed significantly as improved in the supply chain process
automatically improved volume and dependability. Once the supply chain was
managed, the marketing team could also concentrate on creating variation and
flexibility strategies for the customers.
Other
factors that further supported this concept of ‘third place’ was the increase
of passive income opportunities and the availability of free Wi-Fi available at
all their stores. Mobile computing devices with every individual also made
access to the internet possible. This further added to the flexibility that
they provided to the public in general
Starbucks Future Includes More Mobile, More Food, More China, and More Veterans
Recommendations
When
considering the challenges mentioned earlier, the major recommendation here
would be to break down the entire process into smaller sub-parts so that
handling of the operations would be easier. The strategies created here laid
the foundation of the entire process, but for the continuation of effective
handling, sub-departments had to be introduced. The processes also had to
maintain transparency in their operations and hence has to incorporate
procedures so that the supply chain partners maintain transparency and
reliability
Conclusion
The
supply chain management system in Starbucks uses several technologies which are
essential for efficient management. High-quality digital technology with
automated information system is integrated into all its retail stores as well
in various distribution centres and processing plants
References

Comments
Post a Comment